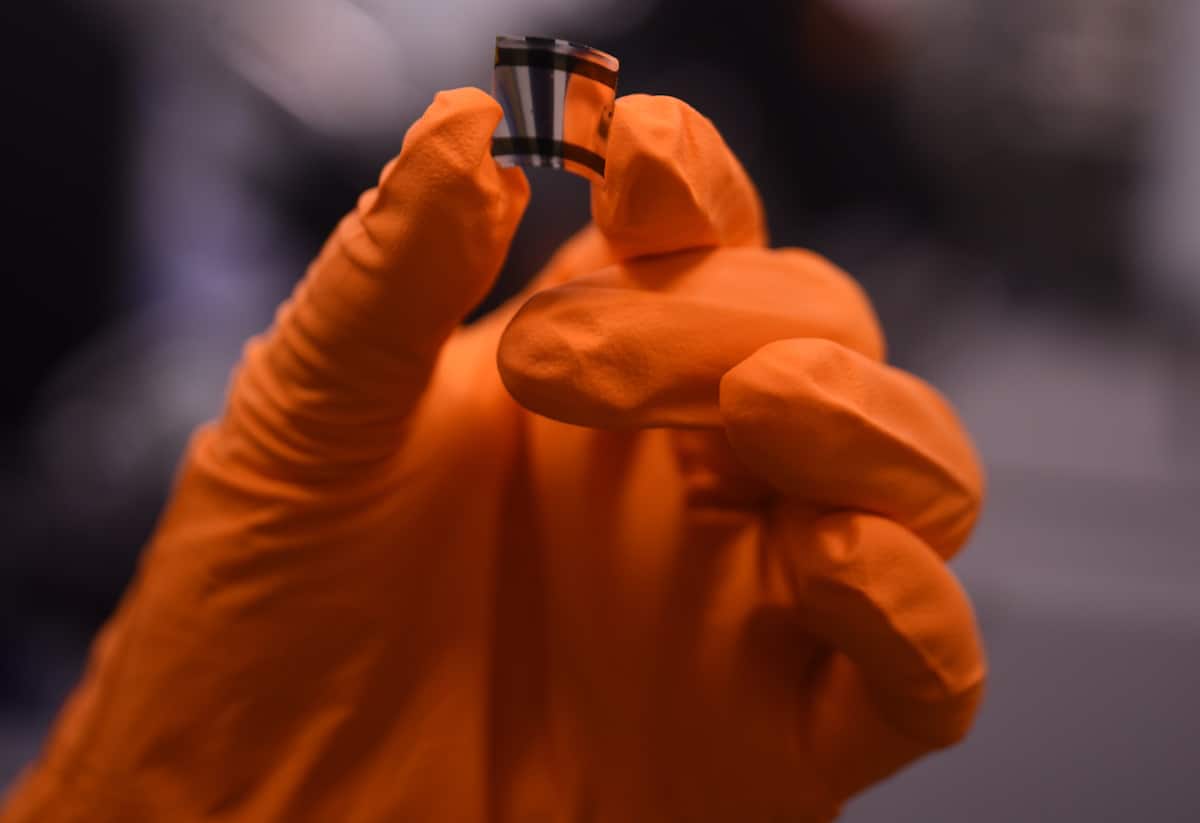Αναζήτηση αναρτήσεων
Πέμπτη 23 Νοεμβρίου 2023
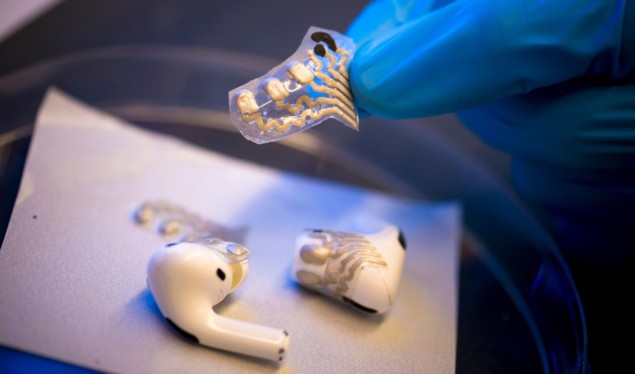
Earbud biosensors provide continuous monitoring of brain activity and lactate levels
A nanoscale device produces a stream of chiral single photons
A nanoscale device produces a stream of chiral single photons
Single-molecule makes a sensitive pressure and force sensor
Single-molecule makes a sensitive pressure and force sensor
Neutral-atom quantum computers are having a moment
Neutral-atom quantum computers are having a moment
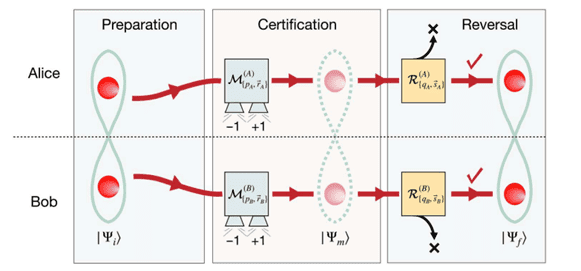
Weak measurement lets quantum physicists have their cake and eat it
Weak measurement lets quantum physicists have their cake and eat it
Shoot-through proton FLASH: a robust approach to brain tumour treatment
Shoot-through proton FLASH: a robust approach to brain tumour treatment
Flexible X-ray detectors line up for medical imaging and radiotherapy
Flexible X-ray detectors line up for medical imaging and radiotherapy
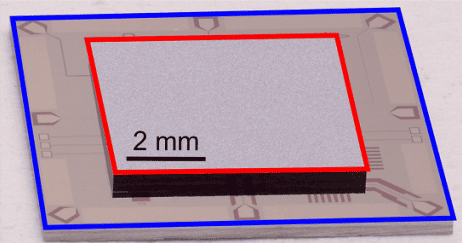
New chip architecture offers hope for scaling up superconducting qubit arrays
New chip architecture offers hope for scaling up superconducting qubit arrays
Biomedical ethicists call for rules governing human research in commercial spaceflight
Biomedical ethicists call for rules governing human research in commercial spaceflight
New telecoms satellites will degrade our view of the cosmos
New telecoms satellites will degrade our view of the cosmos
Top-cited work from North America recognized by IOP Publishing
Top-cited work from North America recognized by IOP Publishing
Δευτέρα 20 Νοεμβρίου 2023
WHEN CHITIN IS CANCEROUS TO HUMAN?
There is currently no evidence to suggest that chitin itself is carcinogenic to humans. Chitin is a naturally occurring polysaccharide found in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans, as well as in the cell walls of fungi. It is widely used in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, without any known carcinogenic effects.
IS CHITIN IN THE FORM OF NANOPARTICLES CANCEROUS FOR HUMANS?
IS CHITIN IN THE FORM OF NANOPARTICLES CANCEROUS FOR HUMANS?
Chitin itself is not considered to be carcinogenic for humans. However, it is important to note that the toxicity of chitin nanoparticles can vary depending on their size, shape, and surface characteristics. Some studies have suggested that certain types of nanoparticles, including chitin nanoparticles, may have potential cytotoxic effects. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential health risks associated with chitin nanoparticles. As with any potential exposure to nanoparticles, it is advisable to follow safety guidelines and take necessary precautions when handling or working with them.
There is currently no evidence to suggest that chitin in the form of nanoparticles is carcinogenic to humans. Chitin is a naturally occurring polysaccharide found in the exoskeletons of insects, crustaceans, and fungi. It is commonly used in various industries, including biomedical applications, due to its biocompatibility and biodegradability. However, like any other material, the safety of chitin nanoparticles will depend on factors such as size, shape, surface charge, and dosage. Further research and studies are always necessary to ensure the safety of any new material.
KONSTANTINOS P. TSIANTIS 20/11/2023
The new superconducting nanowire single-photon detector has 400,000 pixels
The new superconducting nanowire single-photon detector has 400,000 pixels
New telecoms satellites will degrade our view of the cosmos
New telecoms satellites will degrade our view of the cosmos
Evidence emerges for a carbon-rich ocean on Europa
Evidence emerges for a carbon-rich ocean on Europa
Physicists Discover a New State of Matter Hidden in The Quantum World
Physicists Discover a New State of Matter Hidden in The Quantum World
 |
Τετάρτη 15 Νοεμβρίου 2023
Cool Copper Collider most environmentally friendly among Higgs factory designs finds study
Cool Copper Collider Most Environmentally Friendly among Higgs Factory Designs Finds study
Electrons accelerated by firing lasers into nanophotonic cavities
Electrons accelerated by firing lasers into nanophotonic cavities
Organic molecule from trees excels at seeding clouds, CERN study reveals
Organic molecule from trees excels at seeding clouds, CERN study reveals
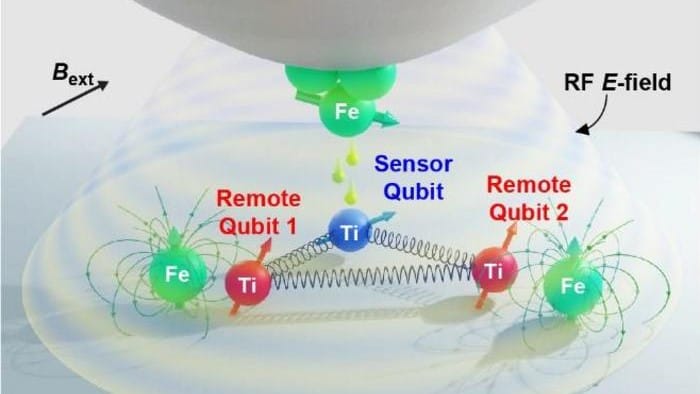
The three-qubit computing platform is made from electron spins
The three-qubit computing platform is made from electron spins
NASA’s Mars Sample Return mission slammed by independent review panel
NASA’s Mars Sample Return mission slammed by independent review panel
Aerosol geoengineering will not stop the Antarctic ice sheet from melting, simulations suggest
Aerosol geoengineering will not stop the Antarctic ice sheet from melting, simulations suggest
Pairs of rogue planets found wandering in the Orion Nebula
Pairs of rogue planets found wandering in the Orion Nebula
Seismic waves reveal complexities in Mars’ mantle
Seismic waves reveal complexities in Mars’ mantle
Multidisciplinary collaboration opens the way to strategic innovation in wireless technology
Multidisciplinary collaboration opens the way to strategic innovation in wireless technology
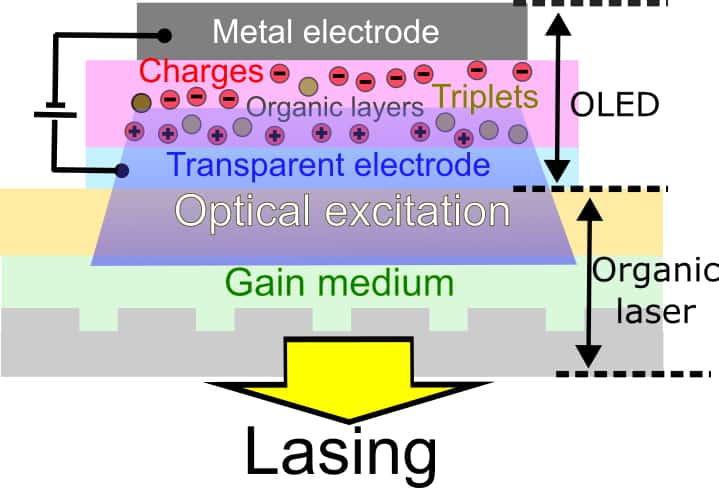
All-electric organic laser is a first
All-electric organic laser is the first
Τρίτη 14 Νοεμβρίου 2023
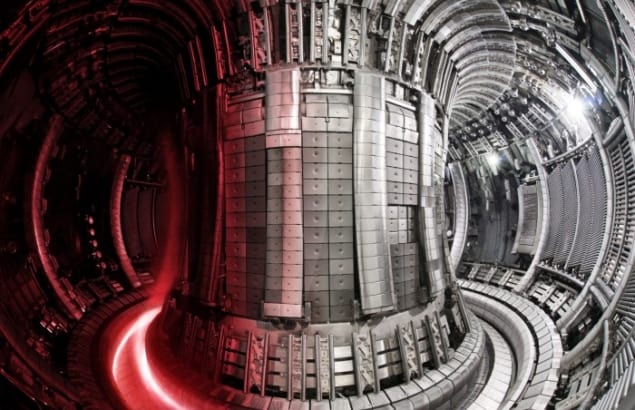
Petition calls on UK to save JET fusion experiment from closure
Petition calls on UK to save JET fusion experiment from closure
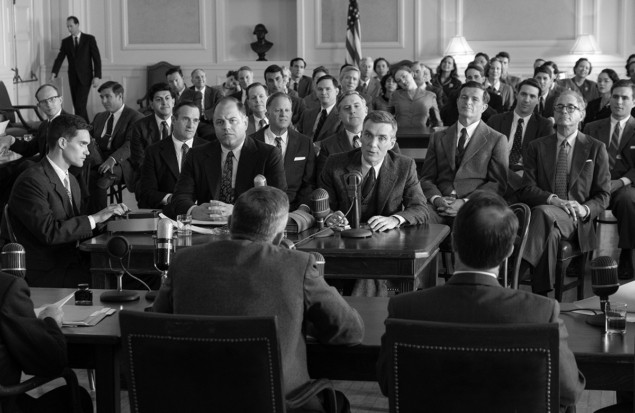
What the movie Oppenheimer can teach today’s politicians about scientific advice
What the movie Oppenheimer can teach today’s politicians about scientific advice
Quantum dot pioneers win Nobel Prize for Chemistry
Quantum dot pioneers win Nobel Prize for Chemistry
A leaky insulating layer reduces battery lifetime
A leaky insulating layer reduces battery lifetime
Electrons caught going around the bend
Electrons caught going around the bend
Κυριακή 12 Νοεμβρίου 2023
Evidence found for the production of tellurium in neutron star mergers
Evidence found for the production of tellurium in neutron star mergers
European Space Agency’s Euclid mission takes its first dazzling images of the cosmos