Kink in cosmic ray spectrum puzzles astrophysicists
15 Feb 2024
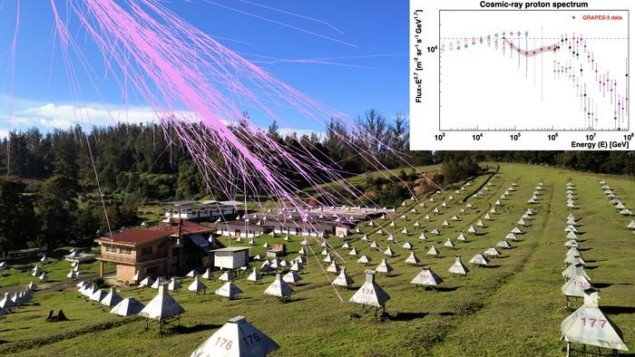
Kinky particles: the GRAPES-3 experiment in Ooty, India depicted with a simulated cosmic ray shower. The inset shows the cosmic ray proton spectrum measurement by GRAPES-3 along with observations by other space and ground-based experiments. (Courtesy: TIFR)
Using observations from the GRAPES-3 muon detector, physicists in India and Japan have explored a poorly understood region of the cosmic ray energy spectrum in unprecedented detail. Fahim Varsi at the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur and colleagues identified a previously unseen feature in the form of a kink in the spectrum.