Quasiparticles called merons appear in a synthetic antiferromagnet for the first time
04 Apr 2024 Isabelle Dumé
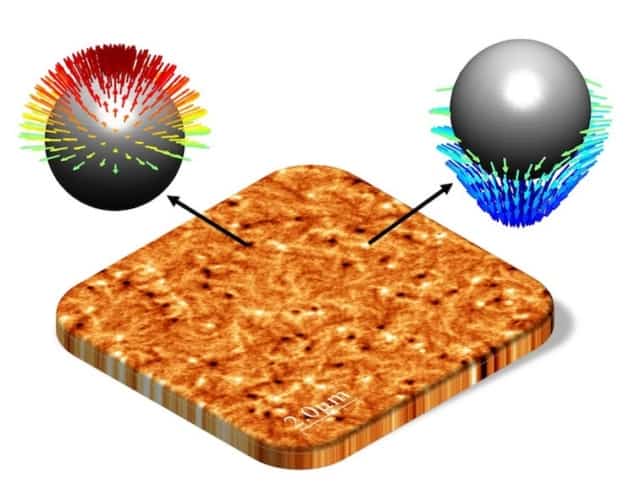
The team observed antiferromagnetic merons and antimerons in a novel "habitat" created by an artificial material. (Courtesy: Mona Bhukta / JGU)
For the first time, an international team of researchers has identified quasiparticles called merons in a synthetic antiferromagnet. The result could lead to new concepts for spintronics devices, which use the electron’s magnetic moment, or spin, to store and process information.
Scientists seek to exploit electron spins in this way because spintronics-based computer memory devices would be faster and more compact than today’s purely electronic ones. The question of how best to build such devices has, as yet, no definitive answer, but much recent research has focused on structures called skyrmions as potential building blocks. These structures are quasiparticles made up of numerous electron spins and can be considered two-dimensional whirls (or “spin textures”) within a material.
Skyrmions exist in many magnetic materials, including cobalt–iron–silicon and the manganese–silicide thin films in which they were first discovered. They are attractive spintronics candidates because they are robust to external perturbations, making them exceptionally stable for storing and processing the information they contain. At just tens of nanometres across, they are much smaller than the magnetic domains used to encode data in today’s disk drives, making them ideal for future data storage technologies such as “racetrack” memories.
Like skyrmions, merons are made up of numerous individual spins. Unlike them, their stray magnetic fields are minuscule, which would facilitate ultrafast operations and even higher information storage densities within a device. Until now, however, merons have only been observed in natural antiferromagnets, where they have proved difficult to analyze and manipulate.
Minimal net magnetic moments
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany; Tohoku University, Japan; and the ALBA Synchrotron Light Facility in Spain have now identified merons in synthetic antiferromagnets made from multilayer stacks of mutually coupled individual ferromagnetic layers. Unlike natural antiferromagnets, these synthetic materials can be prepared well-controlled using established techniques such as sputter deposition.
This exquisite control enabled the team to adjust how the different layers interact, thereby minimizing their net magnetic moments. This gives the system advantages of both antiferromagnets (in which electron spins tend to align antiparallel to each other) and ferromagnets (which have parallel electron spins). Examples include low stray magnetic fields, stable homochiral textures, and fast spin dynamics within a polycrystalline setting, explains Mona Bhukta, a PhD student at JGU and the study’s co-leader.
“In our work, we have successfully stabilized these spin textures in synthetic antiferromagnets with a microscopic easy-plane anisotropy (so that the preferred orientation of the magnetization lies in the film plane) and imaged their intricate structures by combining several imaging methods,” Bukhta says. They used magnetic force microscopy, scanning electron microscopy with polarization analysis, and element-specific photoemission electron microscopy using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism.
The team identified multiple spin textures in the stacked material thanks to these imaging techniques. This was not easy, as the researchers had to image the quasiparticles in a way that resolves all three components of the magnetization vector before they could unequivocally demonstrate the presence of merons. The researchers also developed an analytical model to elucidate the mechanisms that stabilize such structures in their system. The goal, in this case, was to determine the optimal thickness of each layer and identify the best “host materials” for merons.
Related structures also observed
In addition to identifying merons, the team also observed related structures, such as antimony and topologically stabilized bimerons, in their synthetic antiferromagnets. Unlike in skyrmions, the direction of the net magnetization and the emergent field produced by bimerons are mutually orthogonal, Bhukta explains.READ MORE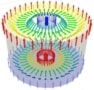

“This characteristic feature enables us, for example, to directly probe and manipulate the topological Hall effect using the meron spin textures,” she tells Physics World. This effect occurs when electrons flow through a conductor in a magnetic field. The applied magnetic field exerts a sideways force on the electrons, leading to a voltage difference proportional to the field's strength. If the conductor has an internal magnetic field or magnetic spin texture, this also affects the electrons.
“The Hall signals from bimerons provide a direct means of detecting and quantifying topology, offering us the exciting possibility to develop magnetic-topology-based technologies in which topology serves as the carrier of information,” Bhukta says.
The researchers, who detail their work in Nature Communications, now plan to investigate the interaction between merons and external magnetic fields and electrical currents. “We would also like to study how they interact among themselves,” Bhukta says.

Isabelle Dumé is a contributing editor to Physics World.
from physicsworld.com 9/4/2024
Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου